10 Key Strategies Every Educator Should Know for Supporting Students with ADHD

|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Introduction
Understanding ADHD is crucial for effectively supporting students in educational settings.
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, presents with symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
By gaining insight into these characteristics, educators can tailor their approaches to better assist affected students.
10 Support Strategies All Educators Should Know
1. Understand ADHD: Learn about the symptoms and characteristics of ADHD, including inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Knowing how ADHD manifests can help you better support affected students.
2. Create a Structured Environment: Establish clear routines and consistent schedules. Structure helps students with ADHD know what to expect and reduces anxiety.
3. Use Visual Aids: Incorporate charts, diagrams, and other visual tools to help explain tasks and concepts. Visual aids can enhance understanding and retention.
4. Break Tasks into Manageable Chunks: Divide larger tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. This makes assignments feel less overwhelming and helps students focus on one thing at a time.
5. Provide Clear and Concise Instructions: Give straightforward and simple instructions. Break them down into single steps when possible to ensure comprehension.
6. Implement Positive Reinforcement: Use praise and rewards to reinforce positive behaviors and achievements. Positive reinforcement can motivate and encourage students with ADHD.
7. Allow for Movement: Recognize the need for physical activity and movement. Incorporate short breaks, physical activities, or even allow students to stand while working when appropriate.
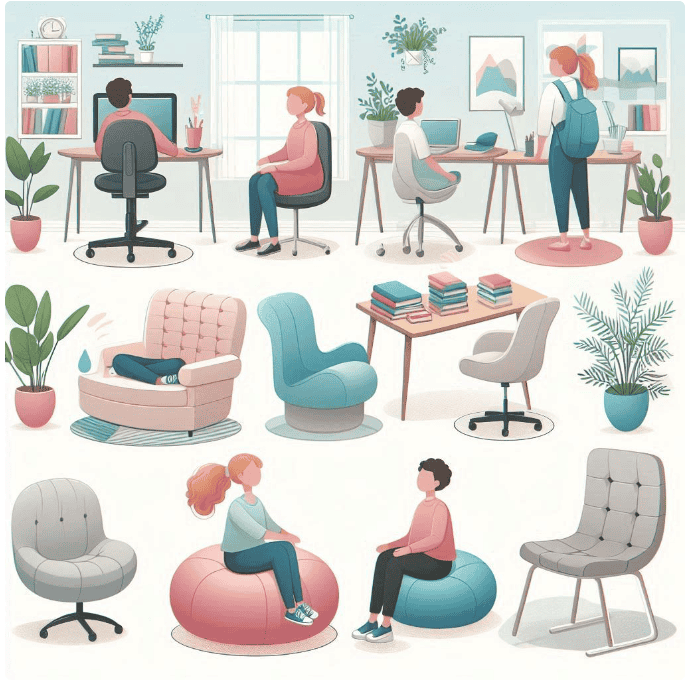
8. Offer Flexible Seating Options: Provide different seating arrangements, such as wiggle chairs, standing desks, or cushions. This can help students with ADHD stay focused by allowing them to move without disrupting the class.

9. Use Assistive Technology: Utilize apps and tools designed to help with organization, time management, and focusing. Tools like timers, planners, and educational software can be beneficial.
10. Communicate with Parents and Specialists: Maintain open lines of communication with parents and collaborate with ADHD specialists. Sharing insights and strategies can provide a more consistent support system for the student.
Conclusion
Implementing these strategies can create a supportive learning environment that helps students with ADHD thrive academically and socially.
By incorporating techniques such as personalized instruction, clear and consistent routines, and a focus on positive reinforcement, educators can address the unique needs of these students.
Additionally, open communication and collaboration between parents, teachers, and support staff is highly encouraged to ensure that students receive the comprehensive support they need.
Integrating technology and interactive learning tools can also enhance engagement and make learning more accessible for children with ADHD.
Video Presentation
References
- Ogundele, M. O., & Ayyash, H. F. (2023). ADHD in children and adolescents: Review of current practice of non-pharmacological and behavioural management. AIMS Public Health, 10(1), 35-51. https://doi.org/10.3934/publichealth.2023004
- Creelman, K. (2021). A literature review of understanding and supporting students with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in the classroom. Northwest Journal of Teacher Education, 16(1), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.15760/nwjte.2021.16.1.3
Sensory Toys for Classroom – Great for Students with ADHD
Rachel Wise is the author and founder of Education and Behavior. Rachel created Education and Behavior in 2014 for adults to have an easy way to access research-based information to support children in the areas of learning, behavior, and social-emotional development. As a survivor of abuse, neglect, and bullying, Rachel slipped through the cracks of her school and community. Education and Behavior hopes to play a role in preventing that from happening to other children. Rachel is also the author of Building Confidence and Improving Behavior in Children: A Guide for Parents and Teachers.
"Children do best when there is consistency within and across settings (i.e., home, school, community). Education and Behavior allows us to maintain that consistency."







